Abstract
Background
Patients (pts) with aggressive B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL) progressing after anti-CD19 chimeric antigen receptor T (CART) cell therapy have poor prognosis and may benefit from new therapy options through clinical trials. However, in a single center report, only 12% of such pts were treated in trials (Chow et al. Am J Hematol, 2019). Identifying the reasons for this low enrollment is needed to design future studies for this population. Here, we evaluated the eligibility criteria for recent landmark trials for relapsed/refractory aggressive B-cell NHL to learn what eligibility barriers are present.
Methods
Pts with aggressive B-cell NHL who received FDA-approved CART cell therapy at Mayo Clinic (Rochester, Arizona, Florida) since 2018 and progressed after CART cell therapy were identified. The potential eligibility for the following key trials was evaluated: a) polatuzumab + bendamustine + rituximab, b) tafasitamab + lenalidomide, c) selinexor and d) loncastuximab. The eligibility for each trial was retrospectively assessed at the time of disease progression after CART cell therapy based on hemoglobin (Hb), absolute neutrophils count (ANC), platelet count (Plt), renal and liver function tests, ECOG performance status (PS), and central nervous system (CNS) involvement.
Results
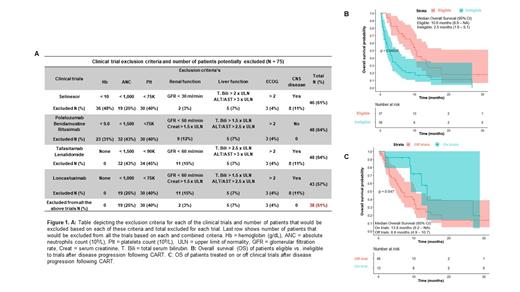
Seventy-five pts had disease progression to axicabtagene ciloleucel (N=73, 97%) or tisagenlecleucel (N=2, 3%) and are included in this analysis. Median time to progression after CART was 2.1 months (IQR: 1.0 - 3.1). Thirteen (17%) pts were treated in clinical trials after progression following CART cell therapy, while 46 (61%) were treated off trials, and 16 (22%) pts never received any treatment after progression. At a median follow-up of 13.6 months (IQR: 9.1 - 26.7) from CART progression, the median overall survival (mOS) from CART progression was 5.8 months (95% CI 3.5 - 10.1) and 53 (71%) pts died.
Thirty-eight pts (51%) did not meet eligibility criteria for any of the 4 recent landmark trials. Hematologic impairment was the most common barrier to inclusion of these patients in clinical trials: Hb < 9 g/dL n=23 (31%) or Hb < 10 g/dL n=36 (48%), ANC < 1.0 x 10 9/L n=19 (25%) or ANC < 1.5 x 10 9/L n=32 (43%), and Plt < 75 x 10 9/L n=30 (40%) or Plt < 90 x 10 9/L n=34 (45%). Renal (n=11, 15%) or liver dysfunction (n=5, 7%), CNS involvement (n=8, 11%) and ECOG PS > 2 (n=3, 4%) were less common reasons leading to exclusion from trials.
Post CART trial ineligible pts had significantly shorter time to progression (median 1.7 months, IQR: 1.0 - 2.6 vs. 3.0 months IQR: 1.9 - 3.4, p < 0.01) and inferior overall response to CART (45% vs 67%, p = 0.06) compared to pts who met trial eligibility post CART. Baseline Hb (median Hb 9.5 g/dL, IQR: 8.5 - 10.5 vs. 10.9 g/dL, IQR: 9.7 - 12.2, p < 0.01) and Plt (median Plt 106 x 10 9/L IQR: 54 - 165 vs. 201 x 10 9/L IQR: 141 - 243, p < 0.01) were also significantly lower in pts ineligible for trials post CART.
There were no significant differences between pts eligible or ineligible for trials with regards to age (median 59 vs. 60 years), number of prior therapies (median 3 vs. 3), prior autologous stem cell transplant (41% vs. 37%), bridging therapy (65% vs. 63%), baseline ANC (median 4,1 vs. 3,0 x10 9/L), or high-grade (grade ≥ 2) cytokine release syndrome (19% vs. 21%) or neurotoxicity (32%, vs. 42%), respectively.
Survival after CART progression was significantly shorter (mOS 2.5 months, 95% CI: 1.6 - 5.1) for the 38 pts ineligible for trials compared to pts eligible for trials (mOS 10.6 months, 95% CI: 8.9 - NA), (p < 0.01). In the 59 pts who received therapy post CART progression, the mOS of pts treated on (n = 13) or off (n = 46) trials was 13.8 months (95% CI: 9.2 - NA) vs. 6.6 months (4.9 - 10.7), respectively (p = 0.047).
Conclusion
Approximately half of the pts (51%) with aggressive B-cell NHL progressing after CART cell therapy would have be excluded from landmark clinical trials. The current hematologic exclusion criteria are a major barrier to enrollment in clinical trials, which would exclude many pts who have disease progression within 3 months of CART cell therapy (ie, primary refractory disease), in whom cytopenia as a toxicity from therapy is prevalent. Given the known delayed hematologic recovery after CART cell therapy and the unmet need of pts progressing to CART cell therapy, the hematologic exclusion criteria should be adjusted to increase trial participation of this population, especially of those with primary refractory disease.
Munoz: Gilead/Kite Pharma, Kyowa, Bayer, Pharmacyclics/Janssen, Seattle Genetics, Acrotech/Aurobindo, Beigene, Verastem, AstraZeneca, Celgene/BMS, Genentech/Roche.: Speakers Bureau; Janssen: Research Funding; Pharmacyclics/Abbvie, Bayer, Gilead/Kite Pharma, Pfizer, Janssen, Juno/Celgene, BMS, Kyowa, Alexion, Beigene, Fosunkite, Innovent, Seattle Genetics, Debiopharm, Karyopharm, Genmab, ADC Therapeutics, Epizyme, Beigene, Servier: Consultancy; Seattle Genetics: Research Funding; Millennium: Research Funding; Pharmacyclics: Research Funding; Genentech: Research Funding; Incyte: Research Funding; Portola: Research Funding; Merck: Research Funding; Celgene: Research Funding; Gilead/Kite Pharma: Research Funding; Bayer: Research Funding; Seattle Genetics: Honoraria; Physicians' Education Resource: Honoraria; Targeted Oncology: Honoraria; OncView: Honoraria; Kyowa: Honoraria. Murthy: CRISPR Therapeutics: Research Funding. Maurer: Morphosys: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Nanostring: Research Funding; Kite Pharma: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Celgene: Research Funding; Genentech: Research Funding; Pfizer: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Bennani: Purdue Pharma: Other: Advisory Board; Daichii Sankyo Inc: Other: Advisory Board; Kyowa Kirin: Other: Advisory Board; Vividion: Other: Advisory Board; Kymera: Other: Advisory Board; Verastem: Other: Advisory Board. Paludo: Karyopharm: Research Funding. Wang: Genentech: Research Funding; Incyte: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; MorphoSys: Research Funding; TG Therapeutics: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Eli Lilly: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; LOXO Oncology: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Novartis: Research Funding; InnoCare: Research Funding. Ansell: Bristol Myers Squibb, ADC Therapeutics, Seattle Genetics, Regeneron, Affimed, AI Therapeutics, Pfizer, Trillium and Takeda: Research Funding. Witzig: Karyopharm Therapeutics, Celgene/BMS, Incyte, Epizyme: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Celgene/BMS, Acerta Pharma, Kura Oncology, Acrotech Biopharma, Karyopharm Therapeutics: Research Funding. Nowakowski: Celgene, NanoString Technologies, MorphoSys: Research Funding; Celgene, MorphoSys, Genentech, Selvita, Debiopharm Group, Kite/Gilead: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Lin: Vineti: Consultancy; Takeda: Research Funding; Sorrento: Consultancy; Novartis: Consultancy; Juno: Consultancy; Legend: Consultancy; Janssen: Consultancy, Research Funding; Bluebird Bio: Consultancy, Research Funding; Celgene: Consultancy, Research Funding; Merck: Research Funding; Gamida Cell: Consultancy; Kite, a Gilead Company: Consultancy, Research Funding.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal